The different grinding solutions you need to know about
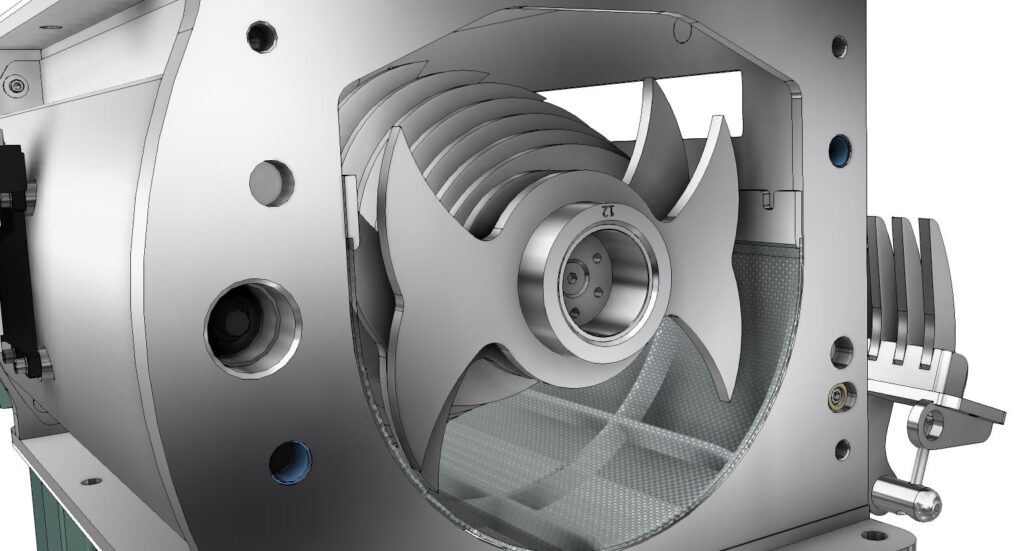
Presentation of the different grinding solutions
Fragmentation in grinding is the process of reducing the particle size of a solid material using various mechanisms. Here are the main forms of fragmentation encountered in grinding:
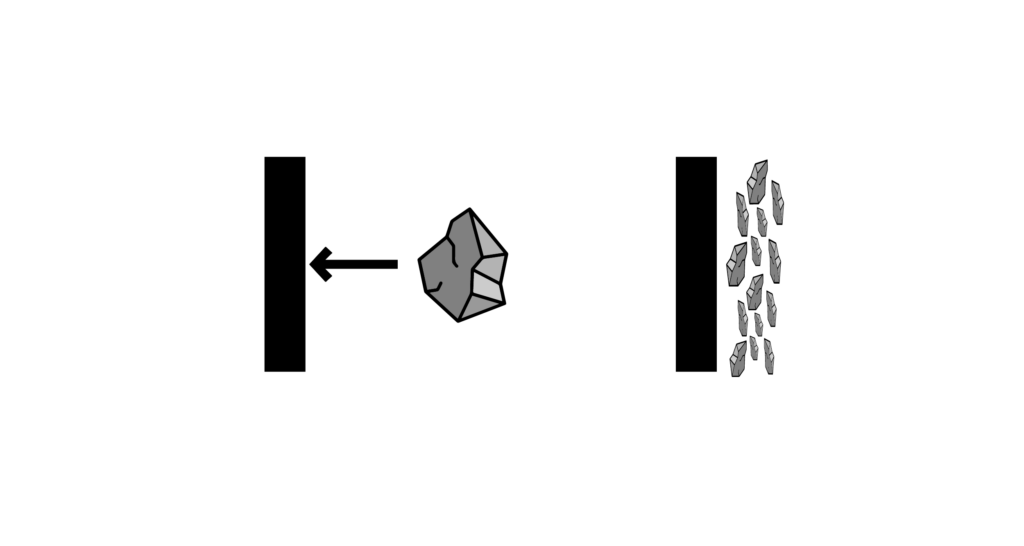
Grinding by impact of the particle on the tool
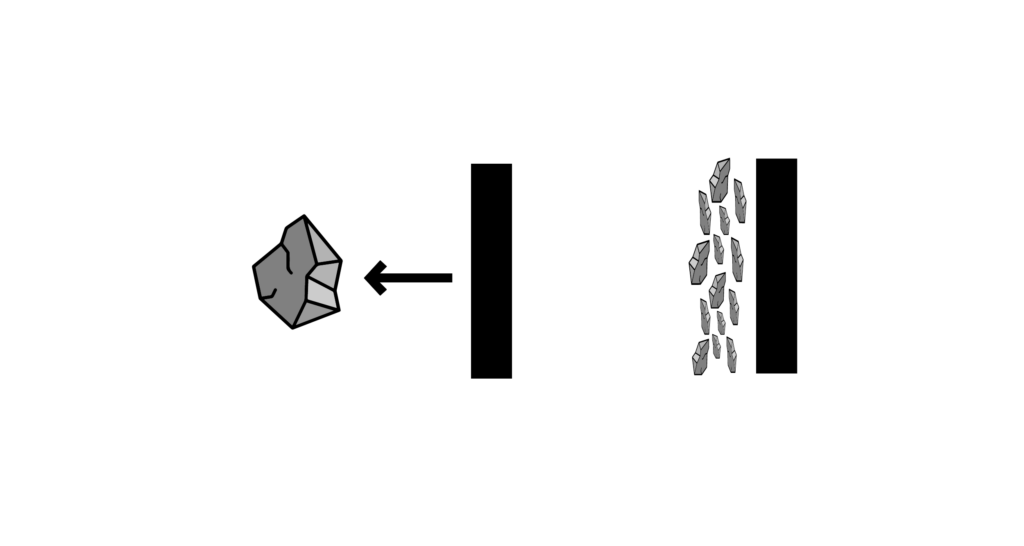
Grinding by moving the tool over the particle
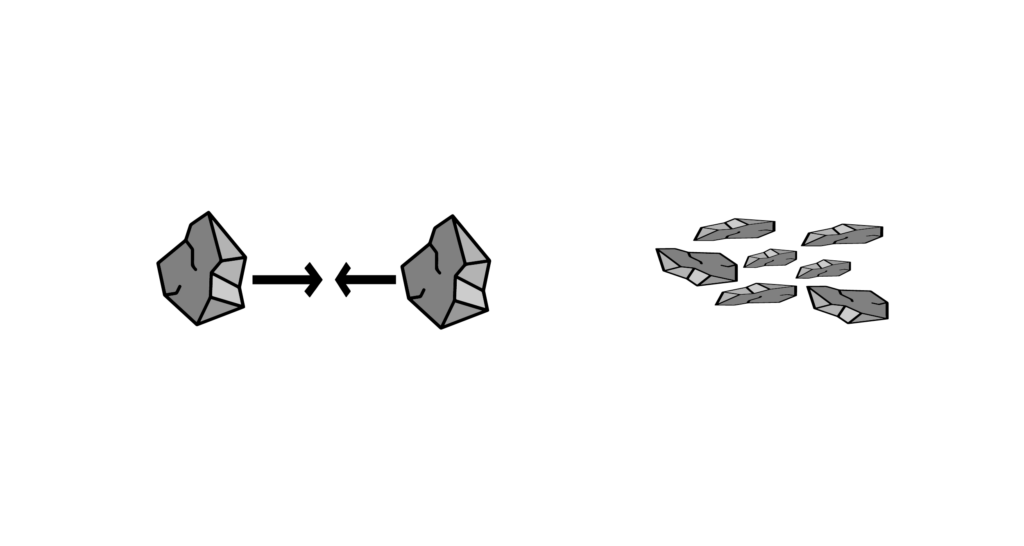
Grinding by impact between particles
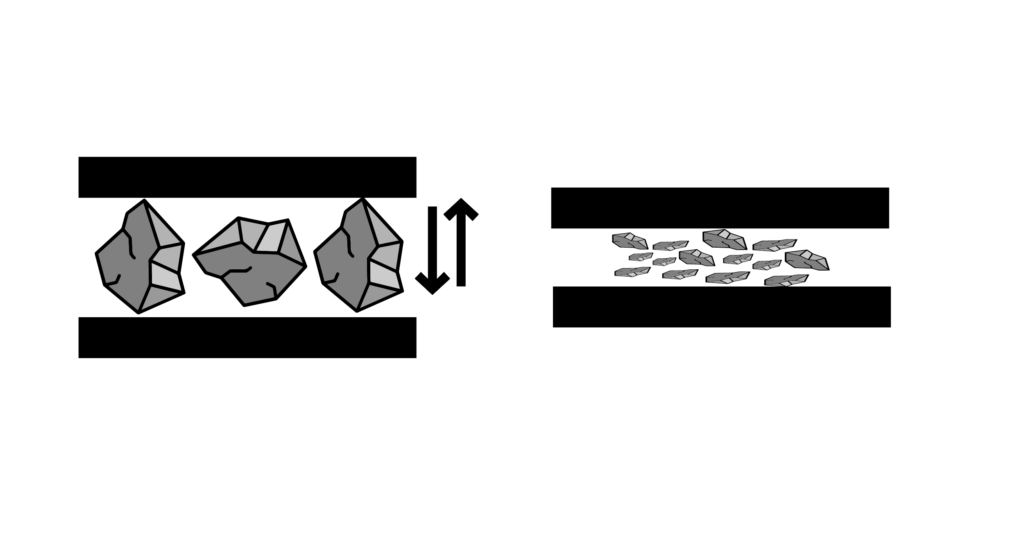
Compression grinding with the tool
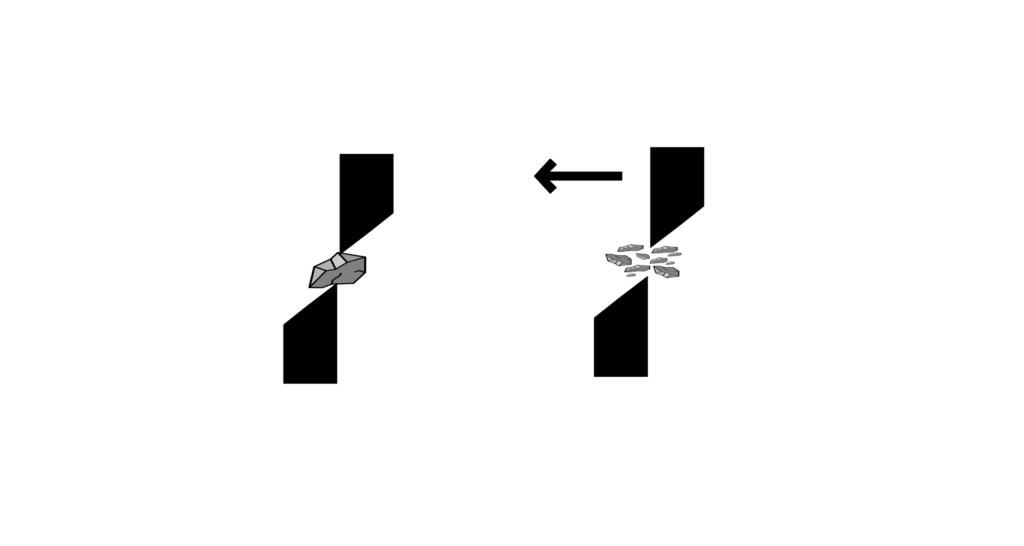
Grinding by shearing
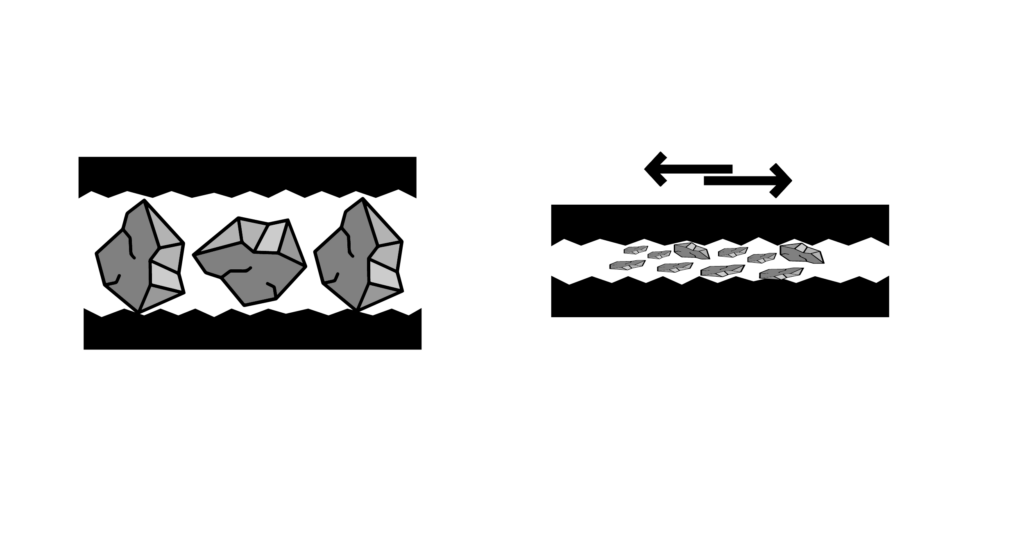
Grinding by abrasion (attrition, friction, shearing)
Different types of fragmentations
Compression
The force is applied in such a way as to compress the material between two surfaces.
Impact
The particles are hit by an external force, causing them to fracture.
Shearing
Shear forces act to separate or tear apart particles.
Abrasion
Progressive wear of the particles occurs when they come into contact with each other or with abrasive surfaces.
Attrition
The particles collide with each other, causing wear and tear and reducing their size.
Friction
The particles are rubbed against each other, generating heat and causing the fracture.
Cryo-grinding
The materials are cooled to cryogenic temperatures to make them more fragile.
Each form of fragmentation has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the material to be processed, the desired final particle size, the properties of the material, and the specific requirements of the application. Some grinding processes can also combine several fragmentation mechanisms to optimise the efficiency and quality of the end result.
Main terms relating to grinding processes
Grinding :
Mechanical process aimed at reducing the particle size of a solid material using various mechanisms such as compression, impact, shear, etc.
Particle distribution size :
The distribution of particle sizes in a sample or material.
Micronization :
Reduction of particle size on the scale of micrometers (microns).
Hammer Mill :
Type of mill using rotating hammers to crush or pulverize materials.
Ball Mill :
Grinding device using metal balls to reduce the particle size in a rotating medium.
Roller Mill :
Mill consisting of two rotating cylinders used to crush or compress materials between them.
Impact Mill :
Mill where particles are struck by hammers or beaters to reduce them in size.
Blade Mill :
Mill where rotating blades cut or chop materials.
Disk Mill :
Mill using rotating disks to reduce materials to fine powder.
Attrition Mill :
Mill where particles collide with each other, causing wear and size reduction.
Cryogenic Mill :
Mill using cryogenic temperatures to make materials brittle and reduce them in size.
Size reduction :
Decrease in the particle size of a material.
Sieving :
Process of separating particles of different sizes through a sieve.
Aggregat :
Solid particle aggregate used in construction, typically derived from the grinding of rocks or similar materials.
Air-Jet Mill :
Mill using an air jet to produce fine particles.
Reduction Ratio :
The reduction ratio measures the size reduction of a material after grinding compared to its initial size. It is usually expressed as a percentage and reflects the efficiency of the grinding process.
Hardness :
The hardness of a material in the context of grinding refers to its resistance to being reduced in size. Harder materials often require more powerful grinding methods.
Friability :
Friability assesses how easily a material can fragment or break. In grinding, friable materials are more easily reduced to smaller particles.
Moisture content :
Moisture content measures the amount of water present in the material. In grinding, high moisture content can influence the viscosity of the material and its behavior during the grinding process.
Dry process :
Dry grinding is done without the addition of water. It is often used for dry materials or when moisture can be avoided for performance or specific finished product reasons.
Energy consumption :
Energy consumption in the context of grinding measures the amount of energy needed to reduce the particle size. It depends on the type of mill, material properties, and the process used (dry or wet). Lower energy consumption is generally desirable for economic and environmental reasons.

Benefit from the advice of the POITTEMILL Group, experts in powder processing, drying and classification technology.
Our laboratory and testing centre offers numerous opportunities to test machines, parameters and processes, at pilot and full scale, to ensure that the quality of your products and the efficiency of your operations generate maximum return on investment for your business.
CONTACT US
A project ? An information ?
At the forefront of innovation, the POITTEMILL Group has been designing its own equipment for over 90 years, offering customised turnkey solutions for powder processing.

